4 Chinese Industrial Robot Stocks to Invest In
Table of contents

China has recently surpassed the US to become the world leader in GDP counted in Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) exchange rates, surpassing both the United States and the European Union. If you’ve forgotten about what PPP is from your college econ classes, it’s a hypothetical rate used to calculate GDP which simply puts everyone on the same playing field. In other words, if both China and the USA produce 10 widgets, they would count as the same output, even if China was able to produce them cheaper. The fact that the Chinese are becoming leaders in almost everything they put their minds to doesn’t come as a surprise given they’ve adopted the complex strategy of working harder – and spending less time on Twitter being outraged about everything.
We’ve talked before about 10 Ways in Which China is Kicking America’s Ass in Tech, and robotics promises to be the 11th one. It’s the cornerstone of the Made in China 2025 government initiative, which aims to upgrade China’s production technology with automation in order to steer Chinese industries away from producing quantity towards producing quality. Robot installations in China (90,000 installations in 2016) make up about a third of the global total.
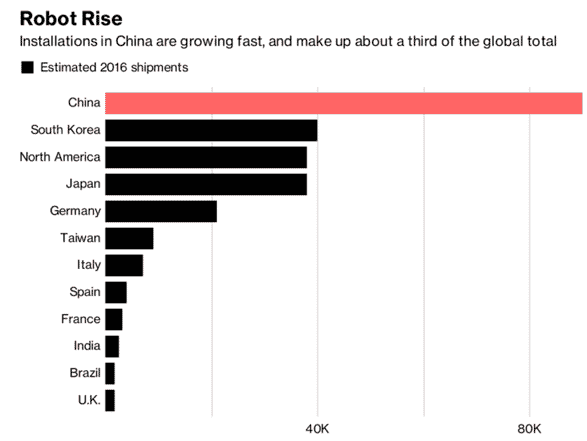
While the absolute number of robots is the highest in the world, the number of robots in China as a percentage of all workers is low. This means that there is plenty of room for expansion. While demand for robots in China is high, most of the demand is filled by international market leaders in robotics such as Fanuc, Kuka or Yaskawa. China’s 5-year Robotics Industry Development Plan aims to address this issue and plans to manufacture 100,000 industrial robots annually by 2020 – all of which already have a place in domestic factories.
While there are a bunch of promising (and well-funded) Chinese startups targeting consumer robotics, we’re interested in getting some investment exposure to any Chinese stocks that will be producing industrial robots for use within the country to match the demand. There happens to be a handful of such companies that retail investors can invest in today, simply by opening an account with Interactive Brokers. Let’s take a look at four Chinese industrial robot stocks.
Estun Automation Co. Ltd. (SHE:002747)
Founded in 1993, Estun Automation Company is a rather small company with a market cap of just $1.2 billion. Established around the time of political reform in China, Estun has grown into a major domestic provider of core controlling parts for high-end equipment as well as full-scale industrial robots using completely proprietary technology.
Shanghai STEP Electric Corp. (SHE:002527)
Founded in 1995, Shanghai STEP Electric Co., Ltd. is a small company with a market cap of just $870 million that provides industrial robots along with control systems and software for industries like welding, packaging, construction and machining.

Shanghai STEP’s strong R&D effort is centered around their Technology Center which offers post-doctoral research opportunities in robotics and has obtained 100 patents so far. The company is also cooperating with the Russians to produce industrial robots in Novosibirsk. Using parts that are assembled in China, the project provides for assembly production and gradual localization of universal 6-axis industrial robots. Shanghai STEP is also expanding production capacity with plans to build a new factory that will produce 10,000 units a year. To put this number in perspective, STEP was able to produce 1,200 robots in the first half of 2017 with their existing factory running at full speed. That means their output should nearly quadruple once the new factory is finished.
SIASUN Robot & Automation Co. Ltd (SHE:300024)
Listed since 2009 October, SIASUN Robot & Automation Co., Ltd. currently has a market cap of $4.23 billion. SIASUN sells industrial robots and automatic assembly & testing production lines for automobile, motorcycle, engineering machinery, and electronics assembly industries, typically as complete turnkey solutions. Besides heavy industry applications, Siasun developed collaborative robots that can work with humans, an underground rescue robot as well as humanoid helpers for interpretation, meal delivery, information sharing and nursing homes.

Last year, following 5 years of development, Siasun opened a $303 million, 340,000-square-foot facility that will produce 10,000 sets of robots annually – joining the line of competitors expanding capacity at the same rate.
Zhejiang Wanfeng Technology Development Co., Ltd. (SHE: 002085)
(Subsidiary of Wanfeng Auto Holding Group)
Zhejiang Wanfeng Technology Development Co., Ltd. was founded in 1992 and is a subsidiary of Wanfeng Auto Holding Group which has a market cap of around $4.8 billion. They offer a very specific industrial robot solution which is used for die-casting materials which do not contain iron. 
While the above companies are expanding production capacity to capitalize on domestic growth, large players in other sectors are bringing robot production in-house, like Amazon did with the acquisition of Kiva Systems in 2012. Besides fulfilling in-house demand, these divisions have significant know-how and research capacity they can use to become major robotics providers in their own right. A few examples of companies that have taken industrial robots in-house are Midea and Foxconn.
Midea Group Co. Ltd. (SHE:000333)
Midea Group was established in 1968 and since then the group has grown into a leading consumer appliances and air conditioning systems manufacturer with global operations and a market cap of $56 billion.
Foxconn Technology Co. Ltd. (TPE:2354)
Founded in 1974, Foxconn Technology Group is a Chinese/Taiwanese multinational electronics contract manufacturing company which is the world’s largest electronics contract manufacturer. Well known for manufacturing the iPhone and other assorted Apple products, it is the fourth-largest information technology company by revenue.

Foxconn is producing 10,000 Foxbots per year currently for their internal consumption and has installed 40,000 of them in Chinese factories so far. This resulted in cutting 60,000 worker positions solving the problem of sustainability and labor force issues in one go.
Conclusion
Currently the investor opportunities for listed Chinese pure play robotics companies are thin. On a more positive note, the country’s drive to achieve better automation through domestic supply has already pushed current players to significantly expand production which may lead to more opportunities for retail investors. Remember how we talked about “robot density” earlier? Here’s a look at how low that number is for China:
That means that there is plenty of room for additional growth in the production of robots domestically. With the recent popularity in Chinese IPOs, the Shanghai-Hong Kong and Shenzen-Hong Kong stock connect programs provide the framework for foreign investors to take part in any new public offerings. Private players like Efort Intelligent Equipment Co could choose to raise capital through a public offering which could lead to more opportunities for retail investors in the future.
Sign up to our newsletter to get more of our great research delivered straight to your inbox!
Nanalyze Weekly includes useful insights written by our team of underpaid MBAs, research on new disruptive technology stocks flying under the radar, and summaries of our recent research. Always 100% free.















